Master's thesis: Generative Adversarial Networks for realistic data augmentation and lesion simulation in x-ray breast imaging
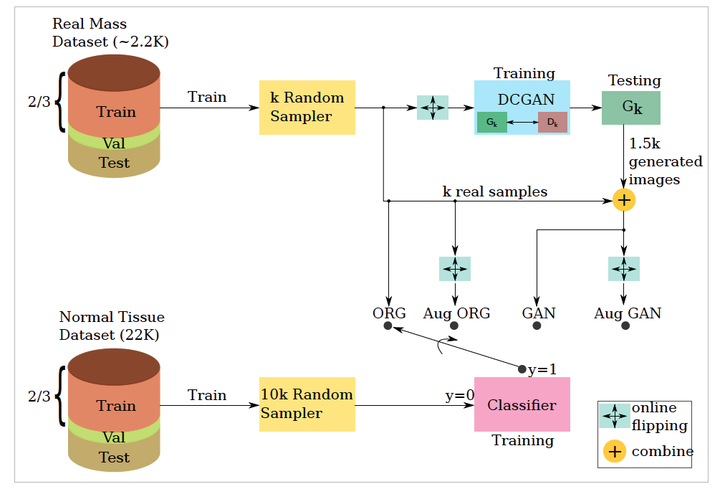 The proposed evaluation framework.
The proposed evaluation framework.Abstract
Early detection of breast cancer has a major contribution to curability, and this importance increases when using noninvasive solutions as mammographic images. Supervised deep learning methods have played a great role in object detection in computer vision, but it suffers from a limiting property; the need to huge labelled data. This becomes stricter when it comes to medical datasets which have high-cost time-consuming annotations. As a leveraging method, Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks (DCGANs) are proposed here to ameliorate this problem, they are trained on different-size partial subsets of one dataset and used to generate diverse and realistic mammographic lesions. The effect of adding these images is tested in an environment where a 1-to-10 imbalanced dataset of lesions and normal tissue is classified by a fully-convolutional neural network. We show that using the synthetic images in this environment outperforms the traditional augmentation method of flipping. A maximum of 0.09 and 0.013 improvement of F1 score and AUC, respectively, were reported by using GANs along with flipping augmentation compared to using the original images even with relatively-small dataset sizes. We show that DCGANs can be used for synthesizing photo-realistic mammographic mass patches with a considerable diversity measured using Frechet Inception Distance (FID).
🧐 Supervisors (great thanks to them): Dr. Robert Marti (robert.marti@udg.edu) and Dr. Oliver Diaz (oliver.diaz@ub.edu).
👉 MAIA website: https://maiamaster.udg.edu/